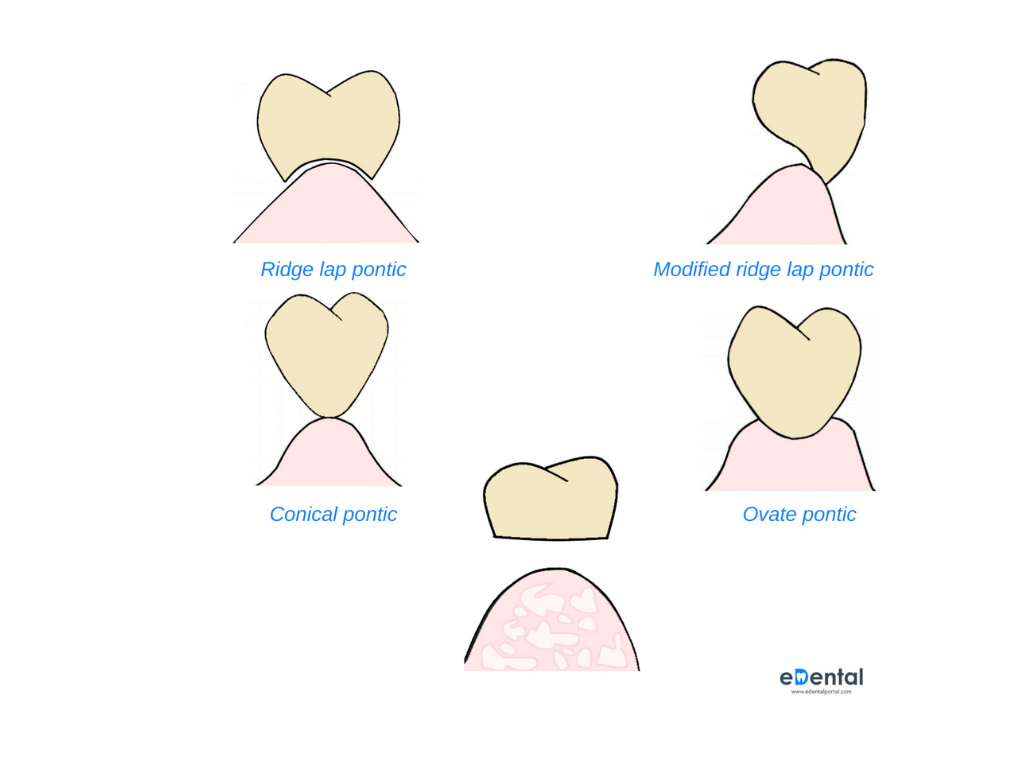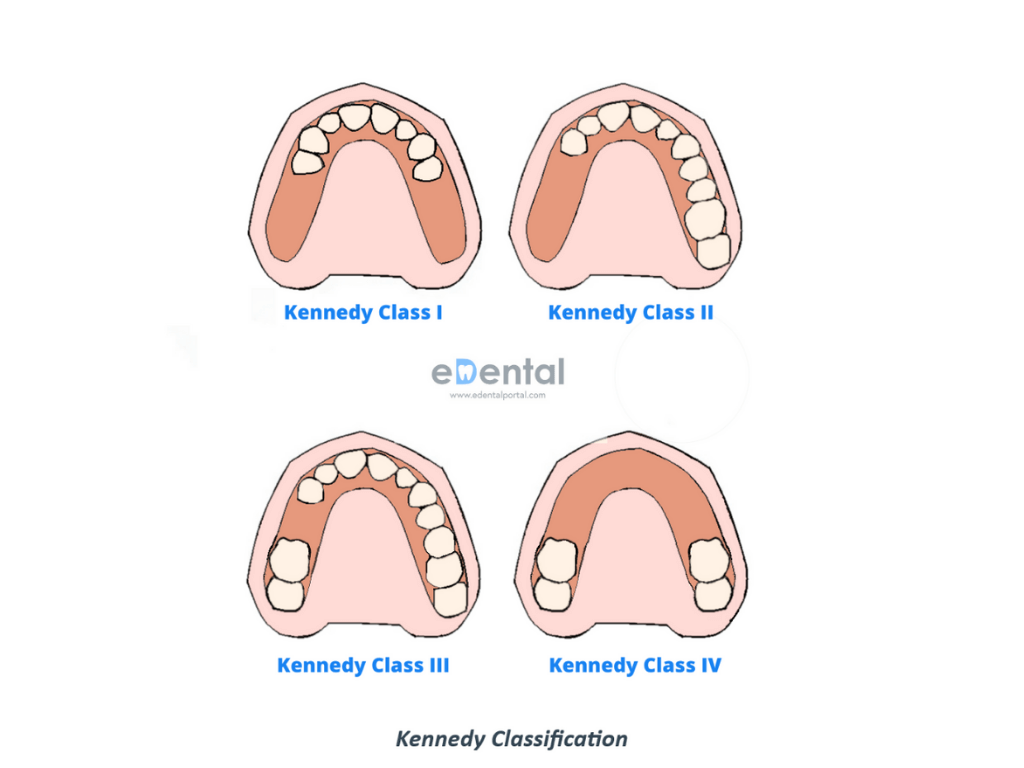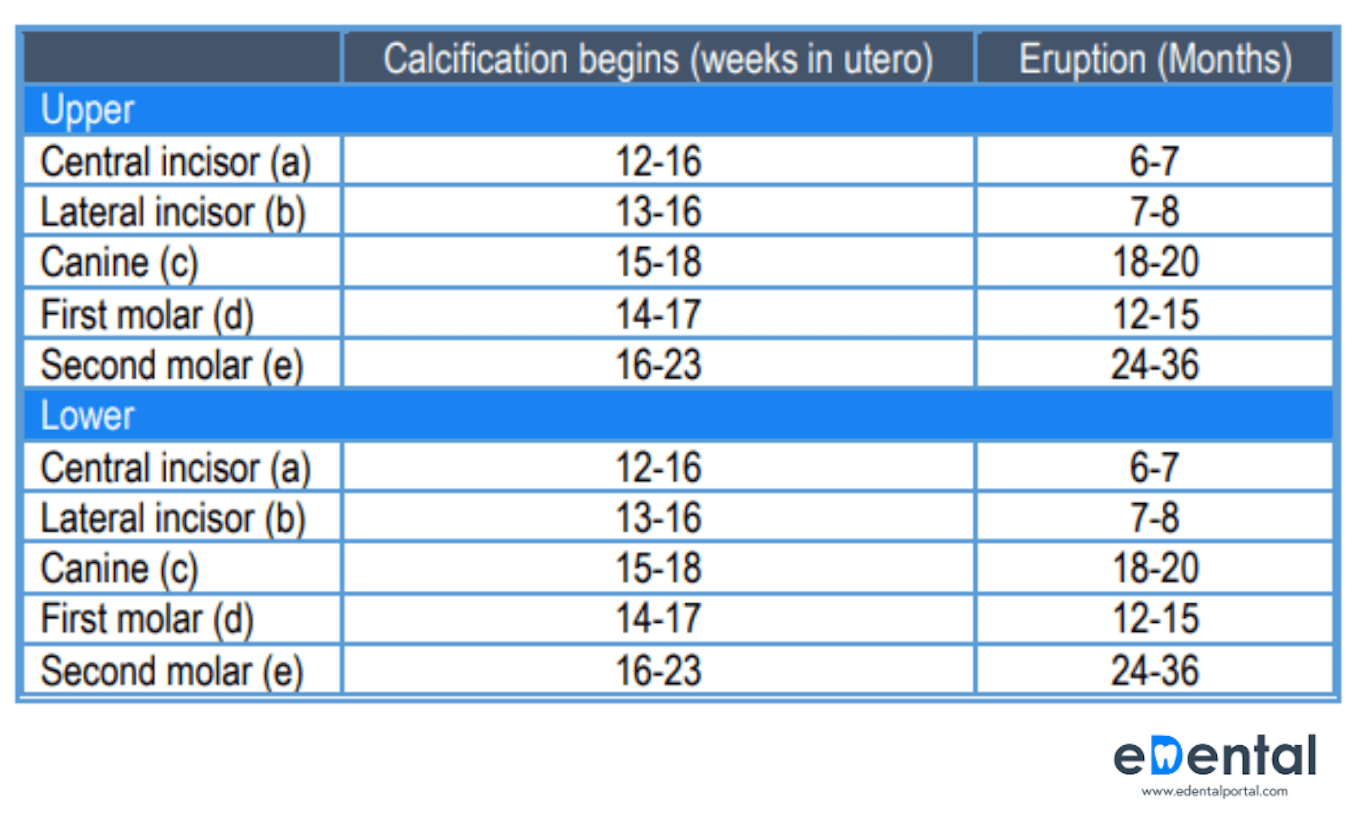
Impression Materials
On 22-10-2021 | Read time about 8 Minutes
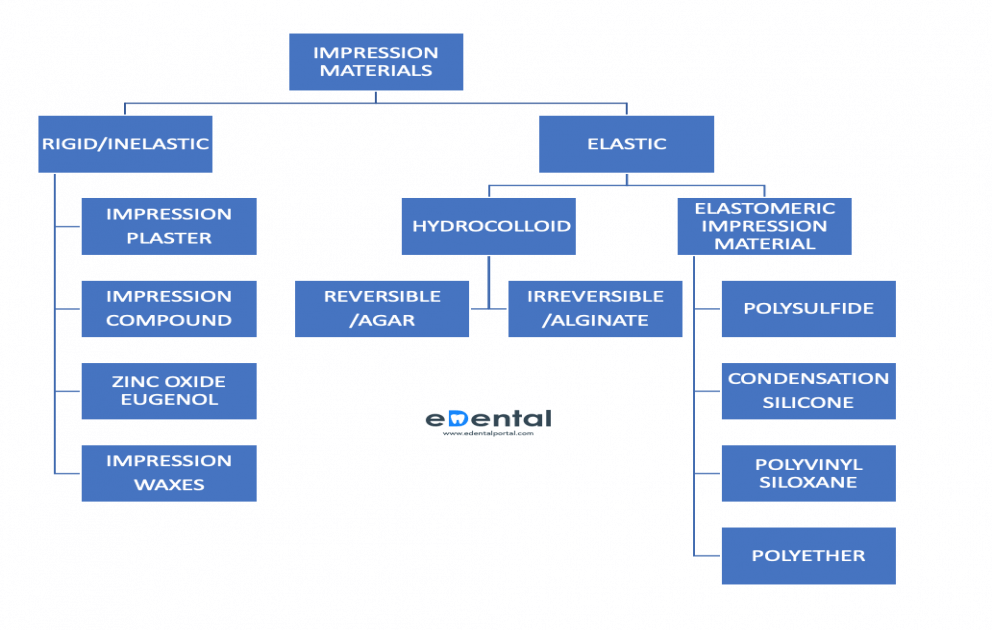
An impression is defined as a negative likeness or copy in reverse of the surface of an object, an imprint of the teeth and adjacent structures for use in dentistry (GPT8). In plain words, a dental impression is a replica of teeth and/or mouth. A replica or impression, a model can be made to be used in the construction of full dentures, partial dentures, crowns, bridges and inlays.Impression materials are classified as above.
INELASTIC IMPRESSION MATERIAL
1. Impression plaster:
They are type 1 dental plaster.
- They are used with a custom tray as a ‘wash impression’.
- Used for making final impressions.
- It is mixed with water in an appropriate ratio, loaded onto a tray and inserted in the patient’s mouth.
- They have minimal tissue distortion.
- They can be easily manipulated and has good flow.
- It is brittle.
- They have minimal accuracy compared to other impression materials, hence rarely used these days.
2. Impression compound:
- They are used for making preliminary impressions with stock trays. Over this primary impression, a secondary impression is made.
- They are also used for border moulding of an acrylic custom tray.
- They are softened with heat and loaded onto a custom tray. This is inserted into the patients mouth while they are soft.
- Low cost and are easy to manipulate.
- Impression can be corrected and repeated as the material is reversible.
- They are rigid and may not record minute details accurately.
- They cannot be used to record final impressions.
- They cannot record undercuts as they are rigid.
- They have high tissue compression.
3. Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE):
- Impression material for edentulous mouth.
- Surgical dressing.
- Bite registration paste.
- Temporary filling material.
- Root canal filling material.
- Cementing medium.
- Temporary relining for dentures.
- They are two tubes, one containing a catalyst(red) and the other a base(white). They are taken in equal amount on a glass slab and mixed to attain a uniform color. The paste is then loaded on the custom tray and final impression is recorded.
- Accurate recording of surface details due to high fluidity.
- They have minimal tissue compression, can be used with minimal pressure technique.
- Cost effective and easy to manipulate.
- They are dimensionally stable.
- Stinging or burning sensation caused by eugenol paste.
- The setting time of the material is affected by humidity and temperature.
4. Impression waxes:
They are not used due to their inaccuracy for final impressions. They are used as a corrective material to refine tray borders.
ELASTIC IMPRESSION MATERIAL:
Elastic impression materials can be easily stretched and rapidly recover their original dimensions when the applied stress is relieved. They are further divided into hydrocolloids and elastomeric impression material.
Hydrocolloids
Reversible hydrocolloid (agar): they are a polysaccharide derived from seaweed.
- they are rarely used to make impressions considering their technique sensitivity and inherent disadvantage.
- They are available are preformed gel. It is liquified at a definite temperature and are placed on impression tray. It is then tempered to a lower temperature that the patient can tolerate, and then is maintained in its fluid state to capture the details of oral structures.
- They are cost effective and has long shelf life.
- The are clean to handle and not messy.
- They do not record fine details accurately.
- They tear easily and may require repeat impressions.
- They have to be poured immediately to avoid distortion.
- They may retard the setting of gypsum material.
Irreversible hydrocolloid(alginate):
- They are widely used due to its ease of manipulation, comfortable for the patient, and relatively inexpensive since it does not require elaborate equipment.
- Alginate impression material is sifted into a rubber bowl containing measured amount of water. The water and powder are incorporated together with a vigorous figure of 8 motion. This is loaded onto a stock tray and impression is recorded before the alginate sets.
- They are cost effective and has a long shelf life.
- Easy to manipulate.
- They do not record fine details accurately.
- They tear easily and may require repeat impressions.
- They have to be poured immediately to avoid distortion.
- They may retard the setting of gypsum material.
Elastomeric impression material
-
Polysulfide: they are also called as Rubber base, mercaptan, thiokol rubber.
- They are not routinely used as they have no obvious advantage over other elastomeric materials and they are dimensionally unstable.
- They are available as a base and catalyst paste which are mixed to polymerize the material.
- They have long working time.
- They have high tear resistance.
- They are reasonably priced.
- They are not dimensionally stable and the cast needs to be poured immediately after impression recording.
- They have very unpleasant odor.
- They stain clothing.
2. Condensation silicone/polysiloxane: this material was developed to overcome the disadvantages of polysulfide.
- They are used for recording impression that require good accuracy like a crown preparation.
- They are available as a base paste and a low-viscosity liquid catalyst which are mixed together to polymerize the material.
- They have a pleasant odor.
- The have optimum working time.
- They can record fine details accurately.
- They are hydrophobic; therefore, the gums and teeth have to be dried of moisture before taking the impression.
- Cast needs to poured immediately after the impressions are taken.
- They have high polymerization shrinkage.
2.Polyvinyl siloxane/addition silicone: they have excellent dimensional accuracy and long-term dimensional stability. These factors make addition silicone the material of choice compared to polysulfide and condensation silicone.
- They are used for recording impression that require good accuracy like a crown preparation.
- They are available as a base paste and a catalyst which are mixed together to polymerize the material.
- They have a pleasant odor.
- The have short setting time.
- They can record fine details accurately.
- They are hydrophobic; therefore, the gums and teeth need to be dried of moisture before taking the impression.
- The putty material is very stiff to handle.
- They do not flow into the sulcus if they are moist.
- They have low tear strength.
- They are very expensive.
3. Polyether:
Use
- They are used for recording impression that require good accuracy like a crown preparation.
- They are available as a base paste and an accelerator paste that are mixed to polymerize the material.
- They are highly dimensionally stable.
- They have high accuracy.
- They have short setting time.
- They have short working time.
- They are very stiff to work with and tear easily.
- They absorb water.
- The undercuts need to be blocked out prior to taking an impression.
- They are the most expensive when compared to all other impression material.
Latest Posts

FREE PROMETRIC PRACTICE TESTS
Try out the most relevant Prometric mock test questions for Dental exams here.
ENROLL NOW